What Is a Cross-Connection?
Understanding the Hidden Risks in Your Plumbing
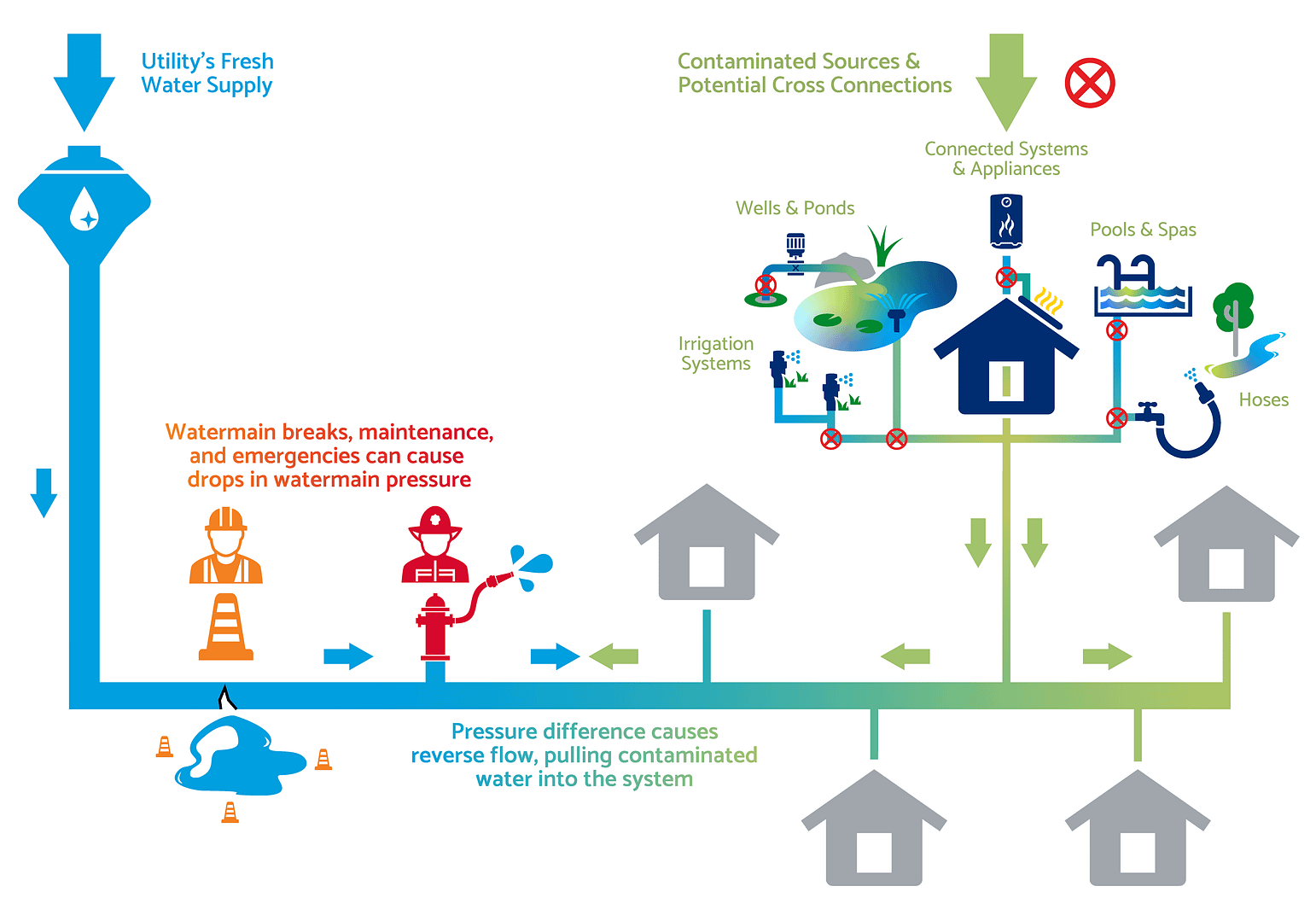
What Is a Cross-Connection?
A cross-connection is a link between a clean water supply and any potential source of contamination. It occurs when the water from a contaminated source, like a pool or industrial system, can flow back into the clean water system. This situation can lead to water contamination, which poses serious health risks. Backflow prevention helps prevent cross-connections by ensuring that water only flows in the intended direction, protecting safe drinking water.
Cross-connections are dangerous because they allow harmful substances, such as chemicals or bacteria, to enter the water supply. Without proper backflow prevention, these contaminants can spread throughout the system, affecting homes, businesses, and communities. To ensure clean and safe drinking water, it’s essential to identify and eliminate any cross-connections.
In many places, local regulations require property owners to install backflow prevention devices. These devices are tested regularly to make sure they are working correctly. In case of any issue, they help maintain the integrity of the water supply. By addressing cross-connections and ensuring backflow prevention, we can keep our water safe and protect public health.
To summarize, understanding and managing cross-connections is vital for backflow prevention. It helps stop water contamination and ensures safe drinking water for everyone.
How Cross-Connections Threaten Water Safety
Cross-connections pose a serious risk to water safety because they can allow contaminants to enter the clean water supply. This happens when there is a link between the public water system and a source of water contamination, like a pool or industrial waste. Without proper backflow prevention, water can flow in the wrong direction, pulling harmful substances into the system.
In fact, even small cross-connections can lead to significant health risks. Contaminants, such as chemicals or bacteria, can spread quickly, compromising safe drinking water for an entire community. That’s why it’s so important to address these issues before they cause problems.
To prevent this, backflow prevention devices are installed at potential cross-connection points. These devices ensure that water flows only in the correct direction, protecting the public water supply. Regular testing of these devices is required in many areas to ensure they are functioning properly.
In summary, cross-connections are a major threat to water safety. They allow contaminants to enter the water system, which can lead to widespread water contamination. By installing backflow prevention systems and addressing cross-connections, we can protect safe drinking water and public health
Common Cross-Connection Scenarios
Residential
In residential areas, cross-connections are more common than you might think. These occur when a link forms between the clean water supply and a contaminated source. For example, a garden hose left in a pool or a sprinkler system can create a cross-connection. If backflow prevention isn’t in place, water can flow backward, carrying harmful contaminants into the clean water system.
Another common scenario is when a home’s plumbing is connected to a water source that’s not properly protected. This could include connections to irrigation systems or a sump pump. Without a backflow prevention device, chemicals, fertilizers, or other contaminants can enter the water supply, leading to water contamination.
To prevent these risks, it’s important to install backflow prevention devices. These devices ensure water flows in the right direction, protecting safe drinking water. Regular testing and maintenance of these devices are essential to keep the water supply safe.
In conclusion, understanding common cross-connection scenarios is crucial to protecting safe drinking water at home. By addressing these issues with proper backflow prevention, you can ensure your water remains clean and safe for your family.
Commercial
In commercial settings, cross-connections can pose serious risks to water safety. For instance, businesses with irrigation systems, cooling towers, or fire suppression systems are at higher risk. If backflow prevention isn’t installed, harmful substances can flow back into the clean water supply, leading to water contamination.
One common scenario is the connection between a business’s plumbing and an irrigation system. Without a backflow prevention device, chemicals or pesticides used for landscaping can contaminate the water supply. Another risk involves boilers or heating systems, where a cross-connection can introduce dangerous materials like rust or scale.
To protect safe drinking water, it’s vital to install and regularly test backflow prevention devices at key points. These devices ensure water flows in the right direction, preventing contamination from entering the system.
In conclusion, businesses must be aware of cross-connection risks. With proper backflow prevention, commercial properties can keep safe drinking water free from harmful contaminants, ensuring public health and compliance with local regulations.
Industrial
In industrial settings, cross-connections are a major concern for water safety. These occur when the clean water supply is linked to a potentially contaminated source. For example, manufacturing facilities may have cooling systems or chemical processes that create cross-connections. Without proper backflow prevention, harmful substances can flow back into the water supply, leading to water contamination.
A common scenario in industrial plants involves water used for cooling or processing. If backflow prevention is not in place, chemicals, oils, or other pollutants could contaminate the clean water system. Another risk occurs when industrial waste or wastewater systems are improperly connected to the water supply.
To ensure safe drinking water, it’s crucial for industries to install backflow prevention devices at critical points. These devices prevent water from flowing backward and protect the entire system from contamination. Regular testing of these devices is also necessary to maintain water safety.
In conclusion, industries must manage cross-connection risks carefully. By using backflow prevention and monitoring the system, they can help protect safe drinking water and avoid dangerous contamination.
Preventing Cross-Connections with Backflow Devices
Cross-connections can allow harmful substances to enter your clean water. When water flows backward due to a pressure drop, it’s called backflow. This can pull chemicals, bacteria, or dirty water into your home’s drinking supply. As a result, it puts safe drinking water at serious risk.
To protect your water, it’s important to use backflow prevention devices. These special valves stop the reverse flow of water. Because of this, they help prevent water contamination in homes, businesses, and even industrial buildings. Common danger points include hose connections, irrigation systems, and heating tanks.
Backflow devices should be installed by trained professionals. In many areas, testing and inspections are also required each year. That way, you’ll know your system is working correctly. If a device fails, repairs or replacements must be made quickly to avoid risks.
By taking these simple steps, you’ll help protect your family and community. Clean water is something we all rely on, so preventing cross-connections with the right equipment matters. After all, backflow prevention isn’t just smart—it’s essential for keeping drinking water safe for everyone.
